Does the Low FODMAP Diet Really Work for IBS? Celiac Disease? The Gluten-Free Diet?
 August 10, 2015 – Data supporting the low FODMAP diet for the treatment of Irritable Bowel Syndrome/Disease (IBS/IBD) is “very limited,” and caution should be used when recommending it to patients, according to a recently published review in the American Journal of Gastroenterology.
August 10, 2015 – Data supporting the low FODMAP diet for the treatment of Irritable Bowel Syndrome/Disease (IBS/IBD) is “very limited,” and caution should be used when recommending it to patients, according to a recently published review in the American Journal of Gastroenterology.
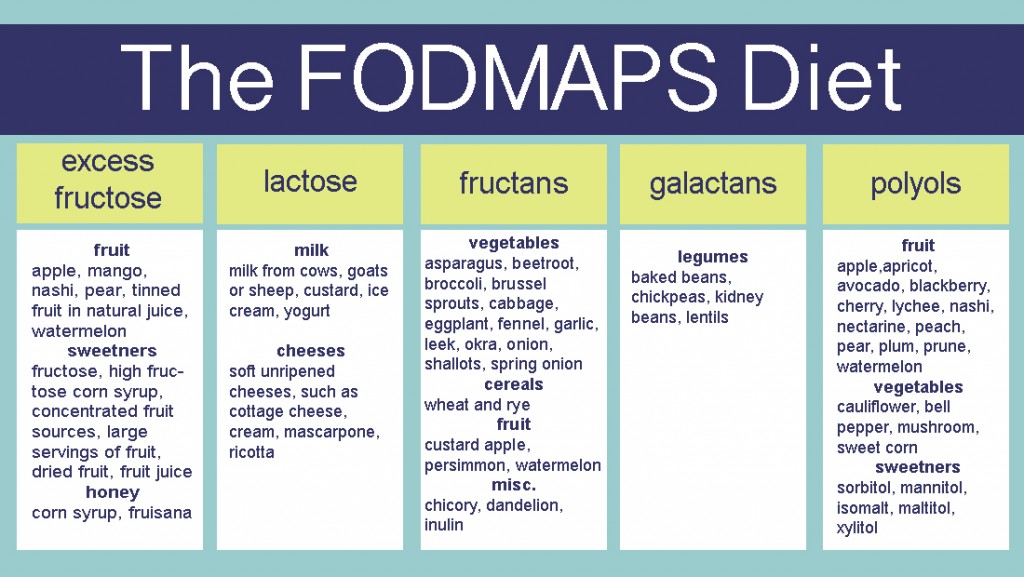
Fermentable Oligosaccharides, Disaccharides, Monosaccharides And Polyols.
Developed in Australia and advocated in recent years for the treatment of IBS, the low FODMAP diet is low in the short-chain carbohydrates found in many, many foods: apples, pears, mangoes, honey, agave syrup, milk products, watermelon, cauliflower, legumes, mushrooms, onion, garlic, wheat, rye, and barley, to name a few. They are also found in some medications and supplements as well as in artificial sweeteners (sorbitol, xylitol, mannitol et al) and also appear in sugar-free or diet drinks, foods, chewing gum, mints and candies.
 It is thought that that FODMAPs are poorly absorbed in the small (upper) intestine and as they proceed to the undigested to the large intestine, are responsible for increase intestinal water volume and are quickly fermented by the bacteria present there. The resulting hydrogen, methane and carbon dioxide increases luminal distension, which may result in pain, bloating and changes in intestinal motility common to those diagnosed with irritable bowel disease and celiac disease. [1]
It is thought that that FODMAPs are poorly absorbed in the small (upper) intestine and as they proceed to the undigested to the large intestine, are responsible for increase intestinal water volume and are quickly fermented by the bacteria present there. The resulting hydrogen, methane and carbon dioxide increases luminal distension, which may result in pain, bloating and changes in intestinal motility common to those diagnosed with irritable bowel disease and celiac disease. [1]
In analyzing a series of studies of efficacy evidence of the low FODMAP diet for the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome, the study found:
 • Efficacy evidence is limited to “a few relatively small, short-term unblinded or single-blinded controlled trials of varying duration,” the review said, though all show some evidence of improved symptoms with few adverse events.
• Efficacy evidence is limited to “a few relatively small, short-term unblinded or single-blinded controlled trials of varying duration,” the review said, though all show some evidence of improved symptoms with few adverse events.
• Two recent review articles analyzing some of the same data had conflicting conclusions; one concluded there is “high quality evidence” supporting the efficacy of low FODMAP diet for IBS, whereas the other “was more cautious in its conclusion.”
• A controlled trial not analyzed in either of these reviews demonstrated a significant improvement in IBS symptoms after 6 weeks of either low FODMAP diet or probiotic supplementation compared with a normal Danish diet (P < .01).
 • Another trial demonstrated low FODMAP diet was associated with lower numbers of bifidobacteria, though the clinical implications of the diet’s impact on gut microbiota are unclear.
• Another trial demonstrated low FODMAP diet was associated with lower numbers of bifidobacteria, though the clinical implications of the diet’s impact on gut microbiota are unclear.
• None of the randomized trials reviewed exceeded a 6 week study period, so long-term effects of low FODMAP diet are unknown.
• Three UK society guidelines were also included in the review and suggest the diet may be appropriate for some patients, but stipulate that advising should be provided by a health care professional with expertise in this kind of dietary management.
The authors concluded they “believe that patients should be advised that there is very limited evidence for” treating IBS symptoms with a low FODMAP diet. “The ideal duration of treatment has not been assessed in a clinical trial and its place in the management of IBS has not been fully established.” – by Adam Leitenberger
1.Could FODMAP Malabsorption Explain Your Persistent Digestive Symptoms Despite Gluten-Free Diet
Our thanks to Healio.com